When you buy through links on our site , we may earn an affiliate mission . Here ’s how it work .
For X , scientists have been bewilder by a mystifying eccentric of antibiotic resistance . call " heteroresistance , " it appears when a tiny fraction of bacterium in a universe can evade antibiotics , and it is almost impossible to detect with routine clinical test . Yet some scientist cerebrate heteroresistance could be the perpetrator behind many antibiotictreatment failure .
Karin Hjort , a microbiologist at Uppsala University in Sweden , is a lead expert on heteroresistance . Live Science spoke with Hjort about what heteroresistance is and what implication it has for the fight against superbugs .

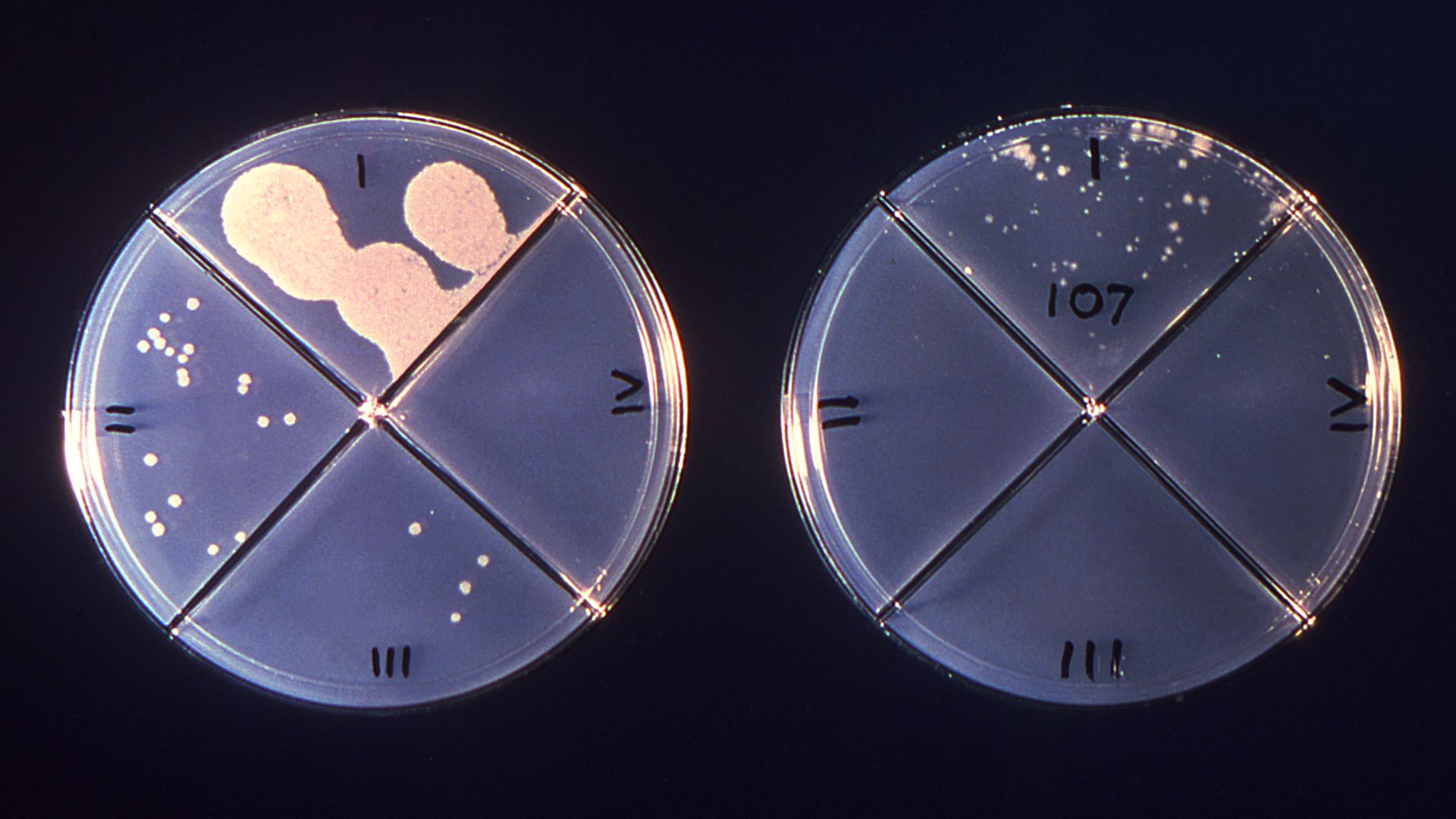
Karin Hjort performed a population analysis profiling in the laboratory. The test is often considered the only reliable method for testing heteroresistance. However, because the technique is very laborious and time-consuming, it is not usually performed in clinical settings.
( This audience has been edit for clarity and length . )
Kristel Tjandra : Can you tell me what heteroresistance is ?
Karin Hjort : The definition of heteroresistance is that you have , within a principally antibiotic - susceptible population , a subpopulation that is insubordinate . This subpopulation should be of a certain sizing . In most cases , it is 10 ^ -7 [ one ten - millionth ] colony - work unit , or executable bacterial cell , per milliliter of stock . The underground level should also be of a certain clock time higher — usually eightfold — than the main population .

Microbiologist Karin Hjort focuses her research on unraveling how bacteria develop heteroresistance.
carat : Is heteroresistance a fresh phenomenon ? How is this different from antibiotic immunity in a general sense ?
KH : It ’s nothing new . Think of it as a type of antibiotic resistance . All the report we have done so far pointed in the same direction : that heteroresistant populations become resistant in the same way that a full universe could become resistant . But the difference here is that this tiny subpopulation can survive higher concentrations of antibiotics than the rest of the population . If you put an antibiotic — survival pressure — that resistant subpopulation will speedily outgrow the others . And when you take aside their selection pressure sensation , the few [ susceptible cells ] that endure without becoming immune will finally outcompete the resistant one .
KT : So , in other words , the population can switch between resistant and susceptible very quickly ?

Karin Hjort is a microbiologist at Uppsala University who has been studying bacterial heteroresistance for more than a decade.
KH : In a gumption , yes .
KT : We run to speak of antibiotic drug - repellent and antibiotic - susceptible bacteria as opprobrious - and - white categories . Is it possible that heteroresistance is this gray area , a midpoint where the bacterium go from being susceptible to becoming resistant ?
KH : Yes , definitely . It could be a way of go from being susceptible to resistant . [ But ] they do n’t become insubordinate unless you plow them with antibiotics . When that happens , the resistant subpopulation live , whereas the main universe that is susceptible dies off the treatment . So , in that sense , you could say that heteroresistance is a step towards resistance . But the isolate will still be heteroresistant the next time we try out them .

relate : Dangerous ' poinsettia strain ' are a growing terror , and antibiotics ca n’t stop their acclivity . What can ?
KT : What do these tests look like ?
KT : From your study , how might bacterium educate heteroresistance ?

KH : Some are resistant because they advance genetic mutation . But instead of everyone in the population being resistant , it ’s only a parcel of the universe that is resistant . There are others that we moot fluid and win their resistance through amplification of factor , which signify that they have higher cistron expression that leads to resistant phenotype .
KT : Can all type of bacteria become heteroresistant ?
KH : I think all bacteria have the ability to become heteroresistant , but the mechanisms can vary .

KT : Can all antibiotic trigger heteroresistance ?
KH : I’m not trusted if all antibiotics really will go to heteroresistance since we have n’t done large enough studies to show that . I mean it count on which antibiotics and bacteria .
Scientists have found a secret ' switch ' that lets bacteria resist antibiotics — and it ’s been bilk research lab test for decades

Read more :
— How fast can antibiotic resistance evolve ?
— 10 of the deadliest superbug that scientist are worried about

— What ’s the remainder between Hans C. J. Gram - positivist and gram - negative bacteria ?
KT : Is heteroresistance something to be worried about in the clinical context ?
KH : Heteroresistance towards some antibiotic drug seems to be uncouth in clinical isolates . And maybe that ’s why discussion betray . Failure could mean that the affected role break down , which I do n’t retrieve is that vulgar because normally , you change to another antibiotic drug . But nonstarter could also think of that the patient role has to stay in the hospital longer , and that is problematic .

KT : What do you hope to see in the futurity with a well understanding of heteroresistance ?
KH : For me , I would like to see in front of me a inclination that tells me whether a strain is heteroresistant towards an antibiotic . And if it ’s heteroresistant , then do n’t treat them with that antibiotic . Basically , it ’s the kind of clinical result for the clinicians to make a intervention decision . Also , [ I go for there will be a way ] to find a way to test these heteroresistant tenor in the infirmary .
We are working on some techniques now to attempt to calculate out better ways of test these [ heteroresistant ] bacterium . You postulate to have something easy and quicker [ than universe analysis profiling ] .